From February 24 to March 24, 2025, a tuberculosis prevention month is being held, timed to coincide with World Tuberculosis Day.

Tuberculosis is a chronic infectious disease caused by Koch’s bacillus. The most common localization of the disease is the lungs, but tuberculosis of bones, joints, skin, liver and other organs is also common.


According to statistics from the World Health Organization, up to 33% of the world’s inhabitants are infected with mycobacteria, and up to 20% have active tuberculosis. Every year, more than 10 million people are diagnosed with tuberculosis in the world, 1.3 million of them die. In Kazakhstan, the incidence of tuberculosis decreased and amounted to 78 cases per 100,000 population in 2022 (in 2000 -171 cases per 100,000 population). In 2024, 397 people fell ill in the Karaganda region (425 in 2023, a decrease of 28 cases).
With the introduction of antibiotics in medicine, the spread and mortality from tuberculosis have been brought under control, but the disease is still on the list of the 10 most common diseases in the world and occupies a leading position in the number of deaths from infectious diseases, overtaking HIV and AIDS.
Reasons
Scientists find traces of tuberculosis in the skeletons of people who lived 5,000 years ago, including Egyptian mummies. The main symptoms of tuberculosis – hemoptysis, exhaustion, and a tearing cough – were described in their treatises by Hippocrates and Avicenna. In the Middle Ages, tuberculosis was commonly known as consumption.
The name of the science of tuberculosis phthisiology was coined by the English scientist Richard Morton and comes from the Greek word phthisis, which translates as exhaustion, consumption.
The causative agent of the disease is Mycobacterium tuberculosis or Koch’s bacillus. This microorganism has a high resistance to most external conditions: it does not die when heated to 90 ° C and cooled to -260 ° C, dried and high humidity. The only physical factor that Mycobacterium is powerless against is ultraviolet radiation – Koch’s bacillus dies after 10-15 minutes of exposure to sunlight. Ultraviolet recirculators have proven effective in the fight against mycobacteria.
Transmission of the pathogen occurs from a sick person. It releases the pathogen into the environment with respiration in case of lung disease, with purulent discharge in case of bone and joint damage, and with urine in case of internal organ disease. In addition to humans, animals, such as cattle, also suffer from tuberculosis. Infection from them is also possible.
Transmission methods
By airborne droplets. Tuberculosis bacteria, along with sputum droplets, are released when coughing, sneezing, or talking. Small droplets can stay in the air for up to 2-3 hours.
By air-dust method. Bacteria released from sputum settle on indoor surfaces, and after drying, they rise into the air along with dust. This can be countered by regular wet cleaning.
Contact number. Koch’s wand settles on all objects used by a sick person and which surround him. For this reason, carpets, soft toys, books and other items that are not subject to wet cleaning must be removed from the ward or room where a tuberculosis patient is located.
From mother to fetus. Intrauterine infection is extremely rare, but possible.
Alimentary. Infection occurs through milk and animal meat infected with mycobacteria. The spread through the body occurs through the gastrointestinal tract and its lymph nodes.
The priority route of infection is the airborne method.


Classification and stages
Tuberculosis is classified on several grounds.
According to the clinical form:
tuberculosis of the lungs;
extrapulmonary forms with lesions of bones and joints, skin, urinary and reproductive systems, lymph nodes, visual organs, etc.;
generalized tuberculosis.
z
According to the degree of contagion:
an open form with active release of mycobacteria into the air;
closed form, in which the patient is a carrier of the infection, but does not spread it.
There are 3 stages in the course of the disease:
Infection. An infectious agent enters the body. At the site of penetration and reproduction of the bacillus, inflammation forms, which involves the nearest lymph nodes. With strong immunity, the disease then passes into stage 2, with weakened immunity – immediately into stage 3.
Latent flow. It is characterized by the gradual formation of foci of inflammation, which stop growing against the background of an active immune response. Such an inactive form can last a long time, but when the immune system deteriorates, it quickly becomes active. The duration of the period ranges from 3 weeks after infection to several years and even decades.
The active form occurs against the background of deterioration of the patient’s condition with the formation of cavities in the lungs and foci of disease in other organs.
The time during which tuberculosis goes from stage 1 to stage 3 depends on the human immune system. It can range from several weeks to several years.
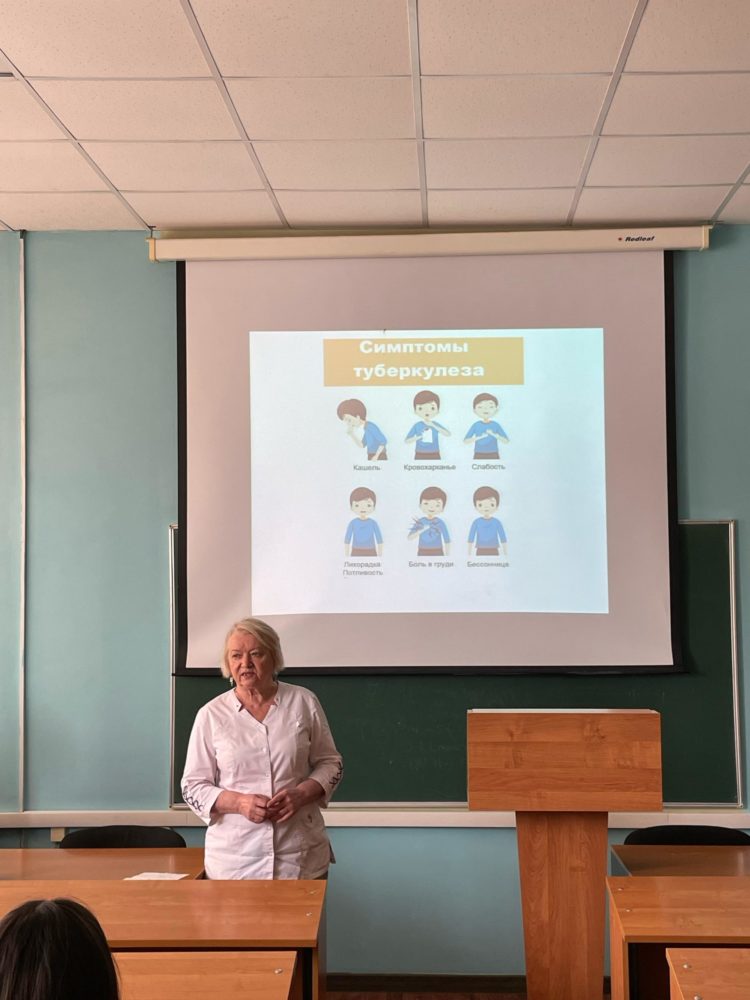
Symptoms
The symptoms of tuberculosis vary depending on the location of the disease. Common symptoms include:
increase in body temperature;
increased fatigue;
loss of appetite and weight;
the appearance of a characteristic blush on the cheeks.
In the case of the pulmonary form, the following characteristic signs are added to the symptoms:
dry or wet prolonged cough;
hemoptysis;
difficulty breathing;
night sweating;
periodic increase in body temperature;
painful sensations in the chest.
Diagnostics



Tuberculosis is diagnosed and treated by phthisiologists. A therapist and a pulmonologist can refer patients to this specialist.
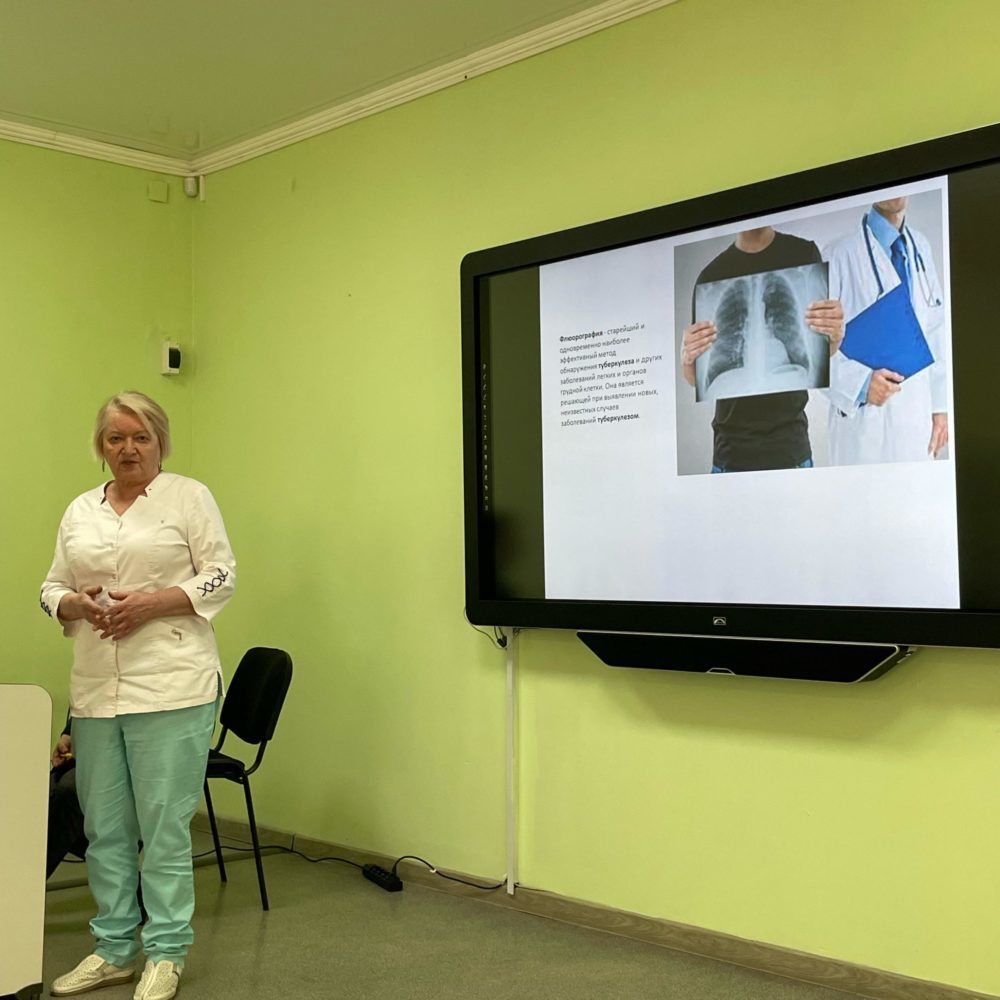
Since the disease can occur for a long time without visible clinical manifestations, special attention is paid to preventive examinations. To detect tuberculosis at an early stage, the following methods are used:
chest fluorography in adults;
Mantoux test or diaskintest in children.
Treatment
Treatment of tuberculosis infection and disease is subject to long-term antibacterial therapy. An effective course of treatment requires taking medications for at least 6 months.
The danger of tuberculosis lies in the fact that even after a successful course of treatment, the body remains:
Mycobacteria in inactive form;
pathological changes in damaged tissues.
For this reason, treatment of the disease should be started as early as possible.
Prevention
It is completely impossible to protect yourself and your loved ones from possible contact with a tuberculosis distributor. However, it is possible to reduce the risk of infection and disease if preventive measures are taken.:
annual fluorography for adults and Mantoux test (or diaskintest) for children;
BCG vaccine delivery to newborns;
balanced and high-quality nutrition;
compliance with the work and rest regime;
regular physical activity;
weight control;
timely access to doctors to prevent chronic diseases;
personal hygiene.
The BCG vaccine does not protect against infection with mycobacteria, but it prevents the development of tuberculous meningitis and disseminated tuberculosis in children. Vaccination is carried out twice – at the age of 3-7 days and at 7 years. The vaccine, which includes a live weakened strain, allows you to gain immunity to the pathogen for up to 20 years.
Preventive measures to combat tuberculosis at the State level also include:
sanitary prevention – examination, disinfection of the premises in which a patient with an identified disease lives or works, identification of a circle of contact persons and their examination;
social prevention – measures aimed at informing the population about the danger of tuberculosis, eliminating poverty, and improving the environmental situation.
The fight against tuberculosis is one of the priorities of States around the world. Therefore, the full range of measures – from prevention to treatment – is funded from the state budget, in 2024, more than 2.4 billion tenge was allocated in Kazakhstan for the treatment of tuberculosis patients.
Timely detection and treatment of the disease ensures that the majority of infected people receive effective treatment and maintain a high standard of living.